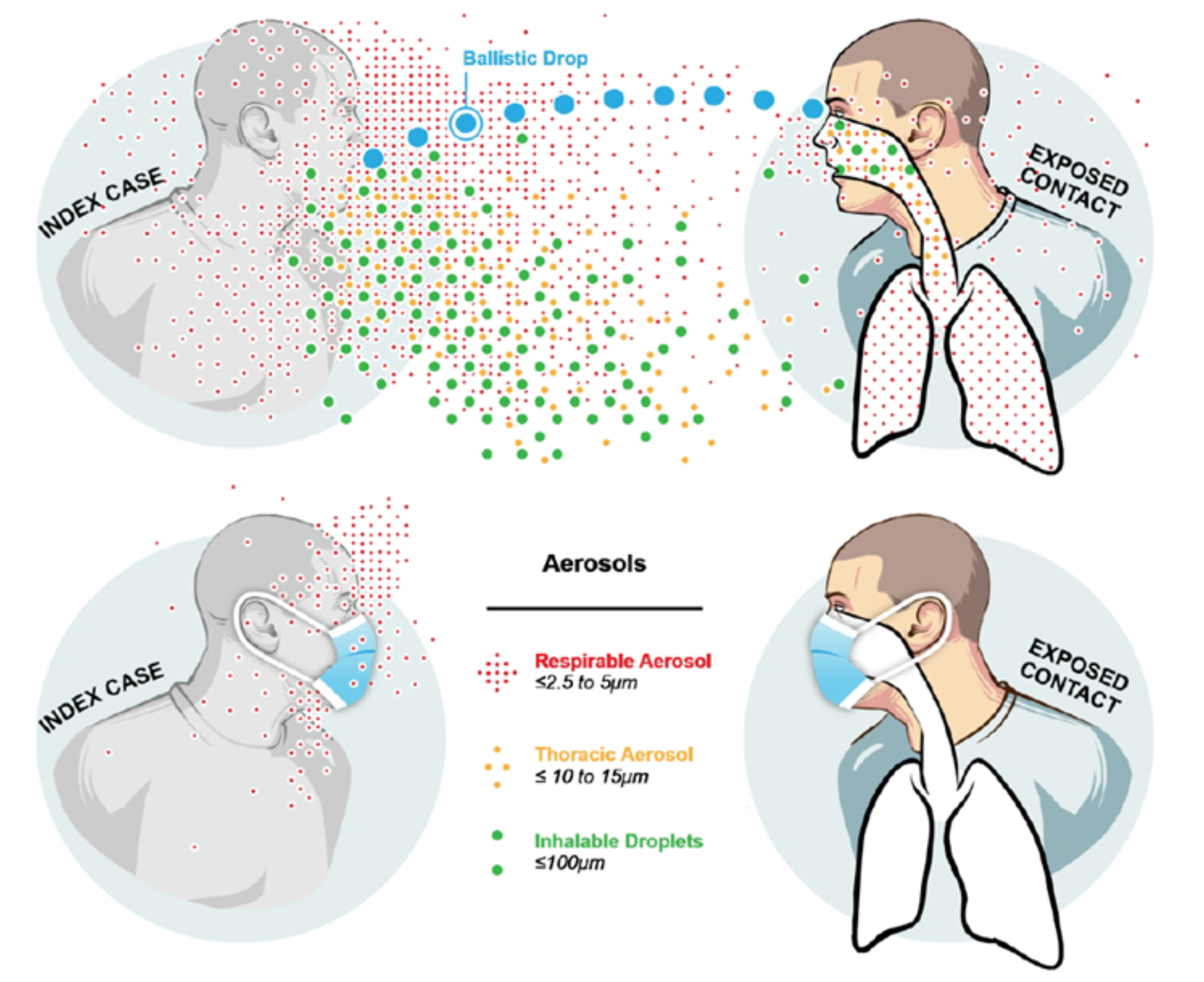
Airborne disease control is a critical area of public health that focuses on understanding and mitigating the transmission of pathogens through the air we breathe. Pioneering research by figures like William Firth Wells has highlighted how airborne pathogens can contribute significantly to outbreaks of diseases, necessitating scientifically informed strategies for their control. Despite the historical struggle for acceptance of these concepts—where scientists like Wells grappled with their own personalities and societal perceptions—the importance of combating airborne diseases remains paramount. With advances in scientific research and a renewed focus on health policies, effective measures and public awareness can help curtail the spread of airborne infections. As health crises arise globally, the lessons from past research drive the ongoing efforts in airborne disease control, ensuring a healthier future for all.
The management of air-transmitted illnesses is an essential component of health safety strategies, encompassing methods to hinder the spread of infectious agents through the atmosphere. This field, entwined with public health initiatives, looks at various factors affecting disease transmission dynamics, particularly in urban settings where densely populated areas amplify risks. Historical figures in this domain, alongside contemporary researchers, have laid foundational theories and practices that guide our understanding of how infections can circulate in the air we share. As we navigate a world increasingly aware of airborne contagions, fostering robust strategies becomes imperative in safeguarding communities from potential outbreaks. In this context, the legacy of innovative scientists and their contributions to air quality and health spans both past discoveries and future solutions.
The Legacy of William Firth Wells in Airborne Disease Research
William Firth Wells made significant contributions to our understanding of airborne diseases, despite facing personal and professional challenges. His research laid the groundwork for comprehending how airborne pathogens can be spread through human exhalations. In the early 20th century, Wells utilized innovative methods, including a centrifuge, to collect samples of air. By demonstrating microbial spread through the atmosphere, he challenged prevailing notions about disease transmission primarily being linked to water or food. This groundbreaking work has shaped public health policies and sparked scientific interest in mitigating airborne pathogens.
Despite his key findings, Wells often found himself at odds with more charismatic personalities in the scientific community, which may have hindered the acceptance of his theories. The negative perceptions of his lecture style and demeanor led to misunderstandings about the value of his research. This highlights a crucial aspect of public health: the communication of scientific ideas can be just as important as the science itself. Understanding these dynamics is essential for fostering dialogue about disease prevention, especially as we navigate the complexities of airborne infections in contemporary public health.
Airborne Disease Control: Challenges and Solutions
Effective airborne disease control is vital in public health, particularly in the face of emerging threats like viral pandemics. The principles of Wells’ research are more relevant than ever. Today’s scientists continue to explore advanced methods to reduce airborne pathogens through improved ventilation systems, air filtration technologies, and the use of ultraviolet light to disinfect shared spaces. These innovations are not only crucial in healthcare settings but also in schools, offices, and public transport, where the risk of transmission is high.
However, control measures must also account for sociocultural factors influencing public compliance and understanding. Engaging communities through educational programs can demystify airborne diseases, promoting proactive behaviors such as vaccination and proper ventilation practices. As scientists like Carl Zimmer emphasize, the legacy of researchers like Wells reminds us that public understanding of science is essential. The fight against airborne pathogens requires collaboration between scientific research and public health initiatives to ensure safe environments.
The Historical Context of Airborne Diseases
The perception and acknowledgment of airborne diseases have evolved significantly since the early days of public health. Initially, theories of miasmas dominated the landscape, attributing disease to bad air without recognizing the role of microorganisms. Early pioneers like Hippocrates laid the groundwork, but it wasn’t until William Firth Wells and others began empirical research that the scientific community started to accept the idea of airborne pathogens as a legitimate threat. This historical context illustrates the journey from skepticism to acceptance that continues today.
Carl Zimmer’s discussions on the historical challenges faced by researchers like Wells serve as a reminder of the importance of clear communication and public outreach in science. Public health officials must bridge the gap between scientific findings and community awareness to facilitate better disease control. The importance of this historical context cannot be underestimated, as it helps us understand current practices and emphasizes the need for ongoing research and discussion about airborne disease prevention strategies.
Public Health Implications of Airborne Pathogen Research
Research on airborne pathogens has significant implications for public health policy and response strategies. As the global population continues to grow and urban areas become denser, the risk of airborne diseases will likely increase. Recognition of the transmission dynamics associated with airborne pathogens is essential for developing effective intervention strategies. Policymakers can utilize findings from scientific research to shape regulations regarding indoor air quality, vaccination campaigns, and emergency responses to outbreaks.
Moreover, engaging the public in discussions about the risks associated with airborne pathogens can foster goodwill and cooperation with public health initiatives. For instance, educational campaigns that focus on the importance of ventilation and cleanliness can mitigate the spread of diseases in crowded spaces. By drawing upon the history of airborne disease research and the lessons learned from past mistakes, we can better navigate the complexities of modern public health challenges.
The Role of Communication in Scientific Acceptance
The narrative of William Firth Wells highlights the crucial role that scientific communication plays in the acceptance of theories within the public and professional spheres. Zimmer’s critique of Wells’ social skills underscores how personality can impact the dissemination and reception of vital research. Even groundbreaking findings on airborne pathogens can flounder if not communicated effectively. The scientific community must prioritize clarity, approachability, and public engagement in its outreach efforts to enhance public understanding and acceptance of preventative health measures.
Strategies like inclusive discussions and the use of diverse media platforms to relay scientific research can help to demystify complex ideas behind airborne disease transmission. When researchers present their work with enthusiasm and clarity, they increase the chances of garnering public support, ultimately leading to better health outcomes. Therefore, fostering effective communication methods is as critical as the research itself in influencing public health practices.
Innovations in Airborne Disease Prevention
Advancements in technology are transforming how we approach airborne disease prevention. Innovations in air purification systems, including HEPA filters and UV-C light technologies, show promise in reducing airborne pathogens in various environments, from hospitals to public spaces. Researchers today are applying principles rooted in Wells’ early studies to create effective strategies that enhance indoor air quality and protect against infectious diseases. This shift towards a more science-backed understanding of air quality emphasizes the need for continuous support for scientific research.
Moreover, the development of real-time monitoring systems that can detect airborne pathogens has emerged as a tool for preemptive measures in public health. These innovations not only contribute to safer environments but also reinforce the importance of research in advancing health technology. As we observe the evolution of airborne disease control strategies, it becomes increasingly apparent that ongoing research and innovation are critical to our ability to respond effectively to future challenges.
The Importance of Cross-Disciplinary Research
Cross-disciplinary research plays a pivotal role in the advancement of airborne disease understanding and control. As Carl Zimmer noted in his discussions, collaboration between microbiologists, public health officials, and social scientists can lead to comprehensive insights that address both the scientific and societal implications of airborne pathogens. By bridging gaps between disciplines, researchers can develop holistic approaches to disease prevention that consider not only the biology of pathogens but also the human behaviors that influence transmission.
Such interdisciplinary cooperation can foster innovative solutions, improving our responses to airborne disease outbreaks through tailored public health campaigns and enhanced educational resources. The lessons learned from historical figures like William Firth Wells remind us that the most effective disease control strategies utilize a multidisciplinary perspective, addressing both the scientific basis of airborne pathogens and the societal factors that influence their spread.
The Future of Airborne Pathogens and Public Health
Looking forward, the future of airborne pathogen research remains uncertain but promising. As new diseases emerge and existing pathogens evolve, it is crucial for scientists to remain vigilant in their studies and for public health officials to adapt to these changes. The insights gained from historical figures like Wells can guide current research efforts, encouraging a proactive approach to understanding how airborne diseases operate and how they can be mitigated through effective policies and community engagement.
Incorporating lessons from the past, including the challenges of effective communication and public acceptance, is vital for ensuring that airborne disease control strategies are well-received. As science progresses, it is imperative to invest in educating both the public and health professionals about airborne transmission, thereby fostering an environment where scientific research can thrive and preventive measures can be effectively implemented.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the significance of William Firth Wells in airborne disease control research?
William Firth Wells played a crucial role in the study of airborne pathogens and the understanding of how diseases can be transmitted through the air. Despite facing challenges due to his personality and conflicts in his career, his research provided compelling evidence of airborne infection and the efficacy of ultraviolet light in controlling airborne pathogens.
How did Carl Zimmer contribute to the public understanding of airborne disease control?
Carl Zimmer, through his book “Air-Borne: The Hidden History of the Life We Breathe,” has highlighted the historical challenges in accepting the airborne transmission of diseases. His work emphasizes the importance of scientific research in airborne disease control and sheds light on key figures like William Firth Wells.
Why is it important to study airborne pathogens for public health?
Studying airborne pathogens is crucial for public health because it helps in understanding how diseases spread through the air, allowing for the development of effective control measures and policies. This research is essential in preventing outbreaks and protecting communities from airborne diseases.
What advancements in airborne disease control were made by Wells and his contemporaries?
Wells made significant advancements in airborne disease control by demonstrating that pathogens could be transmitted via air. He also developed ‘infection chambers’ to study airflow and pathogen spread, and he discovered that ultraviolet light could eliminate airborne pathogens, paving the way for modern infection control strategies.
How does historical research inform current airborne disease control practices?
Historical research, like that of William Firth Wells, informs current airborne disease control practices by illustrating the evolution of our understanding of airborne transmission. Learning from past mistakes and breakthroughs helps inform modern public health strategies and improve responses to current public health challenges.
What historical misconceptions have hindered progress in airborne disease control?
Misconceptions such as the belief that diseases were primarily spread through contact or contaminated surfaces, rather than through the air, hindered progress in airborne disease control. The work of scientists like Wells aimed to correct these misconceptions and promote an understanding of airborne pathogens.
How did the personality of William Firth Wells impact his research on airborne disease control?
William Firth Wells’s personality significantly affected his research on airborne disease control. His often off-putting demeanor and conflicts with colleagues led to missed opportunities for collaboration and recognition, which ultimately slowed the acceptance and application of his groundbreaking findings in the field.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Carl Zimmer’s Theory | Carl Zimmer discusses how the personality of researchers like William Firth Wells may have impeded public acceptance of airborne disease control. |
| Historical Context | The concept of airborne pathogens has been known since ancient Greece, but was often overlooked for centuries. |
| Wells’ Contributions | Wells conducted innovative experiments that provided evidence of airborne transmission of pathogens, including work on UV light’s efficacy. |
| Challenges Faced by Wells | Wells’ unappealing personality and conflicts with superiors hindered the acceptance and promotion of his pioneering research. |
| Legacy of Wells | Despite significant contributions, Wells’ work was not fully recognized until after his death, highlighting issues in scientific leadership. |
Summary
Airborne disease control is a critical aspect of public health and has been significantly influenced by the personalities of researchers throughout history. The story of William Firth Wells illustrates how personal dynamics can impact the acceptance of groundbreaking scientific concepts. While Wells pioneered research into airborne pathogens and their implications for disease transmission, his often difficult demeanor and conflicts with others stifled broader acceptance of his work. Understanding these historical challenges is crucial for fostering a culture that encourages innovative research and public trust in airborne disease control methodologies today.