Is sugar addictive? This question has sparked considerable debate among nutrition experts, drawing comparisons to other well-known addictive substances like alcohol and nicotine. While it’s clear that sugar can trigger cravings and lead to compulsive eating, the scientific community remains divided on its classification as an addictive substance. The health risks of sugar consumption, particularly from ultra-processed foods laden with added sugars, can lead to withdrawal-like symptoms such as headaches and anxiety when consumption suddenly decreases. Understanding these sugar cravings is crucial for making informed sugar consumption recommendations that prioritize long-term health.
The discourse surrounding sugar and its potential addictive qualities often involves examining its impact on our eating behaviors and overall health. Many individuals report experiencing strong urges for sweet foods, mirroring the cravings typically associated with more severe addictive substances. This raises important questions about the psychological and physiological effects of sugar on the body, including withdrawal symptoms that some may experience after reducing their intake. As society grapples with these issues, considering terms like ‘sweetness dependency’ and ‘food addiction’ can further illuminate how our bodies and minds respond to sugar in our diets. Ultimately, fostering awareness of the effects of excessive sugar can guide healthier eating choices.
Understanding Sugar Addiction
The concept of sugar addiction has gained traction in recent years, with many researchers exploring the psychological and physical effects that sugar has on our bodies. While sugar increases cravings and can lead to compulsive eating behaviors akin to addiction, it doesn’t meet the strict clinical criteria that define addictive substances like alcohol, nicotine, or opioids. Despite this, the argument that sugar has addictive qualities cannot be entirely dismissed. The effects of habitual sugar consumption often lead to significant cravings, which can mirror the withdrawal symptoms experienced by those abstaining from more commonly recognized drugs.
The notion of sugar being classified as addictive can lead to confusion. Unlike substances that we can completely eliminate from our lives — such as nicotine or alcohol — sugar is a natural carbohydrate found in various essential foods, including fruits, vegetables, and dairy products. Therefore, understanding sugar’s role in our diets requires a nuanced approach that acknowledges its potential for dependency while recognizing its necessity for nutrition and enjoyment in moderation.
The Science Behind Sugar Cravings
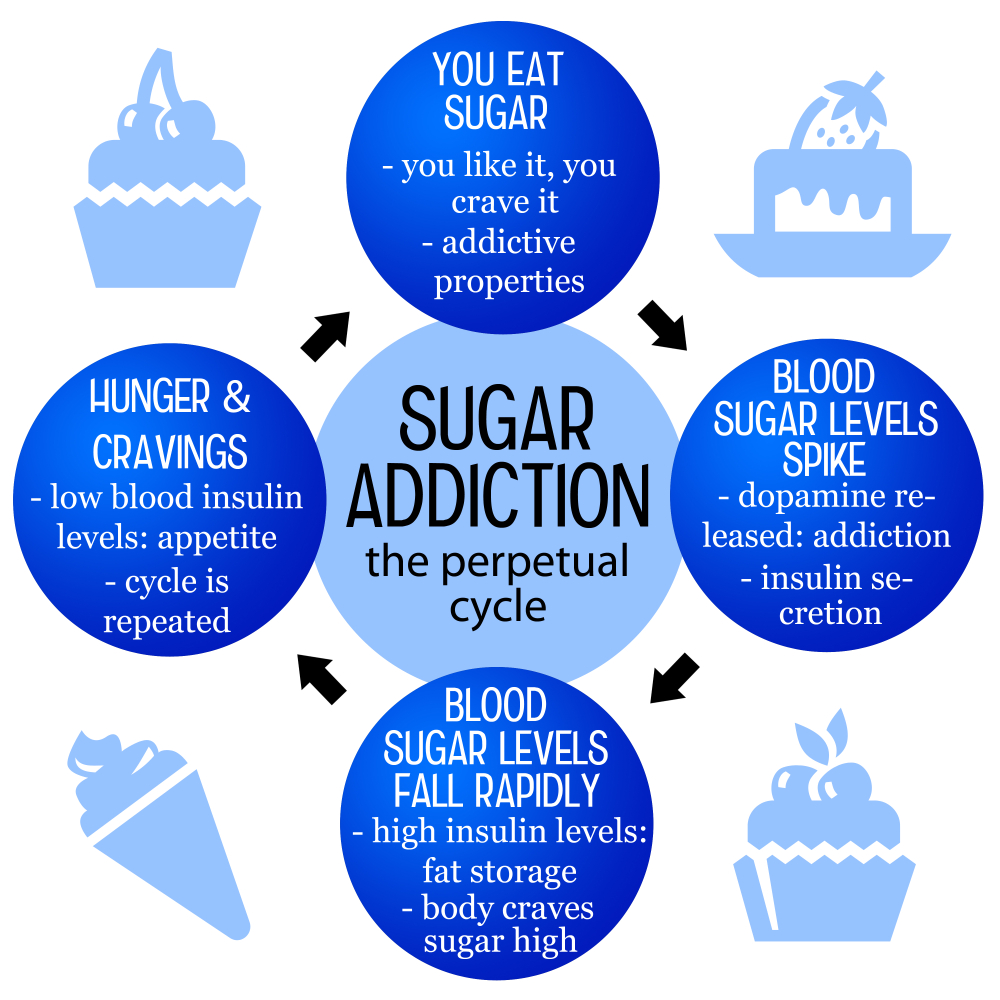
Sugar cravings are a common experience, often driven by the hyper-palatable nature of processed foods rich in sugar, fats, and sodium. These items stimulate the brain’s reward system, triggering the release of pleasure-inducing neurotransmitters like dopamine. Consequently, the more sugar one consumes, the more the craving intensifies, leading to a cycle of increased consumption. Nutrition experts suggest that as we indulge in ultra-processed sugary snacks, we’re more likely to face sugar withdrawal symptoms when trying to cut back, creating a frustrating loop that can be challenging to break.
Research shows that excessive sugar intake not only enhances cravings but can also lead to long-term health risks including obesity, diabetes, and heart disease. Individuals may find themselves trapped in a cycle of craving and consumption, which pushes them to seek out sugary foods even when they are aware of the adverse health implications. The key to managing these cravings lies in gradual reduction rather than complete elimination, as abruptly stopping sugar consumption can lead to a greater risk of withdrawal-like symptoms.
Health Risks of Excessive Sugar Consumption
The health risks associated with high sugar consumption are well-documented and concerning. The American Heart Association recommends significantly lower daily limits for added sugars — no more than 9 teaspoons for men, 6 for women, and much less for children. Exceeding these recommendations can lead to a variety of health issues, including metabolic syndrome, increased risk of cardiovascular diseases, and even certain cancers. The average American consumes nearly 20 teaspoons daily, primarily from sugary drinks and snacks, which is far above these recommended limits.
In addition to physical health ramifications, excessive sugar intake can also contribute to psychological effects. Fluctuating blood sugar levels can lead to increased anxiety, mood swings, and irritability, creating a vicious cycle that drives individuals back to sugary foods for comfort and the temporary pleasure they provide. Understanding these risks emphasizes the importance of monitoring sugar consumption and making informed dietary choices for enhanced long-term health.
Managing Sugar Withdrawal Symptoms
When individuals decide to reduce their sugar intake, they often encounter withdrawal symptoms that resemble those associated with alcohol or drug cessation. Common symptoms include headaches, dizziness, fatigue, and intense cravings for sugary foods. These symptoms are temporary but can be distressing, causing many to revert back to their previous sugar-heavy diets. It’s crucial to recognize these withdrawal symptoms not as a failure, but as a normal reaction to reducing a well-entrenched source of pleasure and energy.
To mitigate the withdrawal experience, nutritionists recommend a gradual decrease in added sugars rather than an abrupt stop. Incorporating nutritious alternatives or timing meals to prevent extreme hunger can help manage cravings and keep withdrawal symptoms at bay. Foods that provide natural sweetness, such as fruits and whole grains, can also help satisfy sweet needs while providing essential nutrients, easing the transition towards a lower-sugar lifestyle.
Gradual Reduction of Sugar Intake
A practical approach to reducing sugar intake is to implement gradual changes rather than attempting to eliminate sugar completely. Studies show that going ‘cold turkey’ can be counterproductive and may lead to increased cravings and potential relapse into excessive sugar consumption. By slowly decreasing the added sugars in one’s diet, individuals can recalibrate their taste preferences over time, making it easier to enjoy foods with lower sugar content without feelings of deprivation.
By reading food labels and becoming more aware of hidden sugars in processed foods, people can take actionable steps towards healthier eating habits. This method not only helps in managing cravings but also instills a better understanding of nutrition and food choices. Over time, as individuals develop a taste for less sugary foods, they may find themselves naturally preferring balanced meals that contribute to overall well-being.
The Role of Sugar in Our Diet
Sugar does play a role in our diets, primarily as a source of energy and a flavor enhancer. While it is essential to limit added sugars, completely avoiding sugar altogether is neither realistic nor necessary. Moderation is key; enjoying the natural sugars found in fruits and dairy can complement a healthy diet while still providing nutrients our bodies need. The challenge lies in managing the intake of added sugars found in processed foods and understanding how they differ from naturally occurring sugars.
Incorporating a variety of nutrient-rich foods into daily meals can help strike a balance that includes some sugar while prioritizing health. Whole foods can provide the required sweetness without the downsides associated with high levels of added sugars. Ultimately, recognizing the distinction between natural sugars and added sugars allows individuals to enjoy sweet treats in moderation, without facing the unwanted health risks associated with excessive consumption.
Identifying Addictive and Non-Addictive Substances
When exploring the idea of sugar addiction, it’s important to differentiate between substances classified as addictive and those that merely cause cravings. Addictive substances like alcohol, nicotine, and opiates create a chemical dependence that alters brain function and physiology. While sugar may lead to increased cravings and even behavioral patterns resembling addiction, it does not create the same level of physiological dependence, making it a unique case.
Acknowledging that sugar can lead to cravings similar to those caused by addictive substances can help in understanding its impact on health. However, the nuances surrounding sugar consumption highlight the difference in how one can approach dietary modifications compared to quitting drugs or alcohol outright. Promoting a balanced approach where sugar is enjoyed in moderation can prevent the negative consequences associated with high sugar intake while allowing for a satisfying diet.
Sugar Consumption Recommendations
Health organizations offer clear recommendations regarding sugar consumption to mitigate health risks associated with high intake. The American Heart Association advises that adult men limit added sugars to no more than 9 teaspoons per day, while women should aim for 6 teaspoons, and children should consume even less. Following these guidelines can help individuals manage their weight, reduce the risk of chronic diseases, and maintain overall health.
Awareness of sugar intake is essential for making informed food choices. Keeping an eye on food labels, being mindful of portion sizes, and opting for whole foods over ultra-processed items can facilitate adherence to these recommendations. Ultimately, achieving a healthy balance in sugar consumption leads to improved health outcomes while allowing for occasional indulgences without guilt.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is sugar addictive compared to other addictive substances?
While sugar does have some addictive qualities, it is not classified as an addictive substance like alcohol or nicotine. Research shows that sugar can lead to cravings and compulsive eating behavior, but these effects do not reach the severity associated with true addiction. Understanding the health risks of sugar can help balance sweet consumption.
What are the sugar withdrawal symptoms when cutting back on sugar?
When individuals reduce sugar intake, they may experience sugar withdrawal symptoms similar to those seen with addictive substances. Symptoms can include headaches, anxiety, and irritability. It is generally advised to gradually reduce sugar consumption to mitigate these withdrawal effects.
How do sugar cravings impact health, and what recommendations exist for sugar consumption?
Sugar cravings often arise from the consumption of ultra-processed foods, which can lead to habitual intake. To promote better health, the American Heart Association recommends limiting added sugar to 9 teaspoons for men and 6 for women per day. Being mindful of sugar intake and choosing whole foods can help manage cravings.
What are the worst health risks associated with high sugar consumption?
Excessive sugar consumption is linked to multiple health risks, including obesity, type 2 diabetes, heart disease, and dental issues. While sugar provides energy, high intake from added sugars leads to negative health impacts, emphasizing the need for moderation.
Is there a difference between natural sugars and added sugars regarding addictive properties?
Natural sugars found in fruits, vegetables, and dairy are not considered addictive. In contrast, added sugars found in processed foods can trigger cravings and compulsive behavior, contributing to health risks when consumed in excess. It’s important to distinguish between the two in dietary choices.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Addictiveness Debate | Sugar increases cravings and compulsive eating but is not classified as an addictive substance. |
| Withdrawal Symptoms | Stopping sugar consumption can lead to withdrawal-like symptoms like headaches and anxiety. |
| Comparison with Other Substances | Unlike alcohol or drugs, sugar is necessary for survival and can enhance flavors in food. |
| Average Sugar Consumption | Americans consume around 20 teaspoons of added sugar daily, exceeding recommended limits. |
| Gradual Reduction | It is advised to reduce sugar intake gradually rather than stopping suddenly. |
| Moderate Consumption | Low to moderate sugar intake is not typically harmful; the key issue is the amount consumed. |
Summary
Is sugar addictive? This question has sparked extensive debate among nutrition researchers and health experts. While sugar does possess qualities that may lead to cravings similar to addictive substances, it is not classified as an addictive drug under clinical criteria. Unlike substances like alcohol and nicotine, sugar is a vital component of many foods that we consume daily, including fruits, vegetables, and grains. Therefore, understanding its effects and managing consumption is crucial. Given the average sugar intake is significantly high in the U.S., it’s vital for individuals to educate themselves on dietary habits, reducing excessive sugar gradually rather than eliminating it abruptly to avoid withdrawal symptoms. Overall, while sugar can result in cravings, it’s important to acknowledge its essential role in our diets.