Suicide prevention for older adults is an urgent public health concern as this demographic faces the highest suicide rates of any age group. Recent studies underscore a critical gap in mental health resources tailored specifically for elderly populations, as many well-known organizations overlook their unique needs. With the increasing reliance on digital platforms for support, it’s imperative to enhance online suicide prevention programs that cater to seniors. Factors such as social isolation and a lack of accessible information contribute to this troubling trend, emphasizing the importance of targeted strategies in geriatric mental health. By improving access to resources and fostering community support, we can work together to combat rising suicide rates in older adults and promote their overall well-being.
The pressing issue of suicide among seniors, particularly those aged 75 and older, highlights the necessity for effective elderly suicide prevention strategies. This vulnerable group often encounters numerous barriers when seeking help, from limited mental health services to inadequate online support for seniors. As society progresses towards digital solutions, creating accessible and user-friendly resources is essential to address the unique mental health challenges faced by older adults. Factors such as isolation and inadequate representation in research play a pivotal role in escalating suicide rates in this age bracket. By fostering a supportive environment and increasing awareness around geriatric mental health, we can deliver vital assistance to older individuals in crisis.
Understanding the Urgency of Suicide Prevention for Older Adults
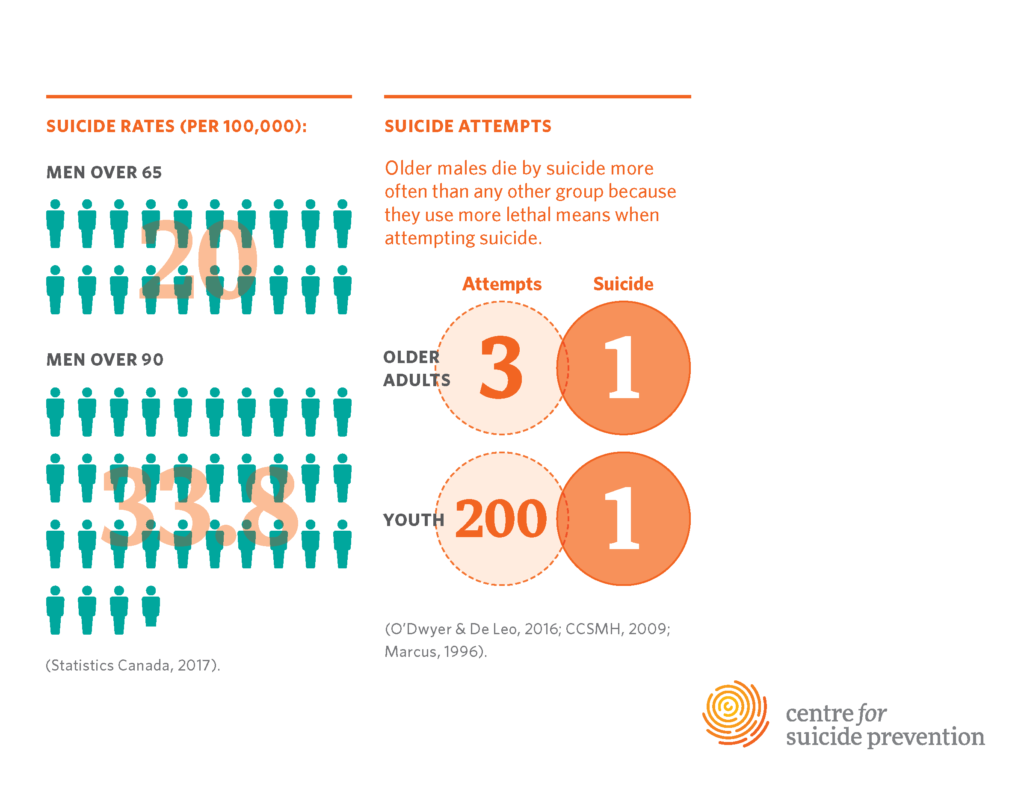
Older adults face a disproportionately high risk of suicide compared to younger demographics. Research indicates that individuals aged 75 and older represent a notably vulnerable population, with suicide rates that are alarmingly high. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, this group experiences rates of approximately 20.3 per 100,000, primarily attributing the rise in suicide among seniors to factors such as social isolation, loneliness, and a general lack of targeted resources that cater specifically to their unique needs.
Despite the clear and urgent need for suicide prevention strategies tailored to older adults, many resources remain out of reach. A recent study from Harvard-affiliated McLean Hospital found that most online platforms either overlook or fail to adequately address the geriatric population. This gap highlights a pressing issue: while younger groups have seen declines in suicide rates, older adults have been left without sufficient support and targeted interventions that take into account their specific mental health challenges.
The Importance of Mental Health Resources for Seniors
Access to mental health resources is crucial for seniors, particularly as they face age-related challenges that can exacerbate feelings of depression and isolation. Mental health resources for older adults must be robust and widely available, ensuring that seniors can find the help they need without friction. Unfortunately, many national organizations fail to provide relevant information that older adults can easily locate and understand, leading to a sense of helplessness among those in need.
Creating tailored mental health resources for seniors involves not just improving accessibility, but also recognizing the specific context of aging. Programs should address the crucial elements of geriatric mental health, such as coping with the loss of loved ones, managing chronic illnesses, and overcoming feelings of isolation. Only by developing resources that resonate with older adults can we tackle the soaring suicide rates in this demographic effectively.
Leveraging Online Support for Seniors
In this digital age, online support has emerged as a vital lifeline for many seniors seeking help for mental health issues, including suicidal thoughts. Studies show that older adults are increasingly turning to the internet to find information about health and wellness, yet the resources that cater to them remain sparse. This emphasizes the need to create effective online support systems specifically designed for older adults, providing them with information that can assist in their mental health journeys.
Well-designed online platforms could offer tailored content that meets the geriatric population’s needs, such as community forums, resource directories, and interactive workshops. By improving the visibility of these resources, we can empower older adults to seek help and engage in meaningful conversations about their mental health. The potential spread of online support can help bridge the gaps in conventional healthcare that have led to high suicide rates among older adults.
Addressing the Imbalance in Suicide Prevention Efforts
A critical finding of the recent study is the stark imbalance in suicide prevention efforts that seem to target younger audiences while neglecting the urgent needs of older adults. Despite the rising suicide rates in older demographics, the resources available are not adequately publicized or accessible. This oversight reveals systemic shortcomings in how mental health initiatives are designed and implemented, highlighting the importance of crafting prevention strategies that speak directly to older adults.
Recognizing this imbalance is only the first step; effective action must follow. Major suicide prevention organizations are urged to reevaluate their outreach strategies, ensuring that they are inclusive of older adults’ needs. By prioritizing this group in their campaigns and employing inclusive language and relatable scenarios, we can create a supportive environment where older individuals feel validated and encouraged to seek help.
The Role of Social Connections in Reducing Suicide Risk
Social connections play a crucial role in mental health, especially for seniors. Feeling connected to family, friends, and community can significantly reduce the risk of suicidal thoughts and behaviors. Engagement in social activities can foster a sense of belonging, thus mitigating feelings of isolation that often accompany aging. Programs designed to help older adults connect with others can directly impact their mental well-being and help lower suicide rates within this demographic.
Creating opportunities for social interaction, whether through community centers, online platforms, or local gatherings, can facilitate these important connections. Strategies must be implemented to ensure older adults have the means to forge relationships and maintain contact with loved ones, thereby enhancing their emotional resilience. Efforts that promote social well-being can lead to improved mental health outcomes, ultimately reducing suicide rates in older adults.
Understanding the Unique Healthcare Needs of Older Adults
Older adults present a distinct set of healthcare needs that differ significantly from those of younger populations. As they experience complex health changes, including cognitive decline and chronic illness, their mental health can greatly suffer. Addressing these unique healthcare challenges is essential for effective suicide prevention. By incorporating comprehensive geriatric mental health strategies into healthcare services, we can better respond to the psychological demands faced by seniors.
Healthcare providers must be trained to recognize the signs of mental distress in older adults, ensuring they employ sensitive and appropriate screening practices. Interventions should be holistic, combining physical health support with mental health resources, allowing for a more complete approach to elder care. Implementing policies that support integrated care models can play a transformative role in reducing the suicide rates within this at-risk population.
The Need for Increased Funding and Research
A significant factor contributing to the lack of resources for older adults in crisis is inadequate funding and research focused on late-life suicide prevention. Much of the existing research centers around younger populations, leaving critical gaps in understanding the factors that lead to suicidal ideation among older adults. Increased investment in research is vital for developing effective prevention programs tailored to the needs of this demographic.
Funding should also be allocated to support outreach initiatives that educate seniors and their families about available mental health resources. By emphasizing the importance of late-life mental health research, stakeholders can work towards creating a comprehensive support system, ultimately paving the way for more effective interventions in preventing suicides among older adults.
Implementing Effective Suicide Prevention Campaigns
Public-facing suicide prevention campaigns have a proven track record of effectiveness, yet there remains a notable absence of these efforts targeted specifically at older adults. Crafting campaigns designed with an understanding of the unique psychological context faced by seniors is crucial for raising awareness and providing necessary resources. Such campaigns should focus on relatable messaging that resonates with older adults and encourages them to both seek help and acknowledge their emotional struggles.
Employing diverse media channels can broaden the reach of these campaigns, ensuring that they connect with seniors where they spend their time—whether online or offline. By utilizing testimonials, educational materials, and accessible resources, these preventive initiatives can spark important conversations about mental health and suicide prevention, ultimately equipping older adults with the tools they need for better mental health outcomes.
Encouraging Family Involvement in Suicide Prevention
Family dynamics play an integral role in the mental health of older adults, making the involvement of loved ones critical in the prevention of suicide. Families can serve as a frontline support system, helping to identify signs of distress and encouraging their elderly relatives to seek help when needed. Recognizing this role underscores the importance of resources aimed not just at seniors, but also at their families, providing education on mental health and effectively communicating around sensitive topics like suicide.
Support programs that engage family members can foster an environment where older adults feel more comfortable discussing their mental health challenges. By equipping families with the right tools and knowledge, they can contribute significantly to reducing the stigma surrounding mental health issues, thereby facilitating more open conversations. Building a collaborative network of support can lead to improved outcomes for older adults at risk of suicide.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the key factors contributing to elderly suicide prevention efforts?
Elderly suicide prevention requires a multifaceted approach that addresses factors such as social isolation, mental health conditions, and accessibility to mental health resources. Understanding these elements is crucial for developing effective strategies tailored to older adults, particularly those over 75 who experience the highest suicide rates.
How can mental health resources support older adults at risk of suicide?
Mental health resources specifically designed for older adults can provide tailored support to address their unique challenges, such as chronic illness, loss, and loneliness. Accessible resources, including therapy, helplines, and online support for seniors, can empower older adults to seek help and foster connections that enhance their mental well-being.
What role does online support for seniors play in suicide prevention?
Online support for seniors plays a vital role in suicide prevention by providing easily accessible platforms where older adults can connect with peers and mental health professionals. These platforms can help combat feelings of isolation and provide essential information on geriatric mental health, ultimately reducing the risk of suicide among this population.
What is the importance of geriatric mental health in preventing suicide among older adults?
Geriatric mental health is critical in preventing suicide as it focuses on the unique psychological and emotional needs of older adults. Tailored interventions that address depression, anxiety, and other mental health issues can significantly decrease suicide rates in older populations by promoting resilience and coping strategies.
Why is there a need for targeted suicide prevention campaigns for older adults?
Targeted suicide prevention campaigns for older adults are essential because this demographic is often overlooked in broader initiatives. Given their unique life circumstances and heightened vulnerability to suicide, customized campaigns can address their specific needs and improve access to appropriate resources and support systems.
What challenges do older adults face when seeking suicide prevention resources?
Older adults often encounter various challenges when seeking suicide prevention resources, including technological barriers, lack of awareness about available services, and societal stigma around mental health issues. These obstacles can prevent them from accessing vital support, making it crucial to enhance resource availability and visibility for this population.
How can community programs enhance elderly suicide prevention efforts?
Community programs can enhance elderly suicide prevention efforts by fostering social engagement, providing educational workshops on mental health, and offering peer support groups. These initiatives create environments that encourage conversation about geriatric mental health and reduce the stigma surrounding suicide, ultimately saving lives.
What interventions have been effective in reducing suicide rates in older adults?
Interventions such as targeted mental health counseling, family support involvement, and community education have proven effective in reducing suicide rates among older adults. Additionally, integrating mental health services with primary care can help identify and manage risks early, leading to better outcomes for at-risk individuals.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| High Suicide Rates | Older adults, especially those 75 and older, have the highest rates of suicide among age groups. |
| Lack of Resources | National organizations do not provide sufficient resources specifically targeting older adults for suicide prevention. |
| Unique Healthcare Needs | Suicide prevention efforts must consider the unique healthcare needs of older adults. |
| Research Findings | A study from McLean Hospital shows that older adults struggle to find online resources for suicide prevention. |
| Importance of Targeted Campaigns | There is a pressing need for public-facing campaigns that specifically address the needs of older adults. |
Summary
Suicide prevention for older adults is an urgent and critical topic that demands immediate attention. With older adults possessing the highest suicide rates, especially those aged 75 and above, it is imperative that we acknowledge and address the scarcity of appropriate resources aimed at this population. The recent findings highlight a significant gap in targeted online efforts, underscoring the necessity for campaigns and programs tailored to their specific healthcare needs. By increasing accessibility to suicide prevention resources, we can ultimately save lives and provide the support older adults truly need.