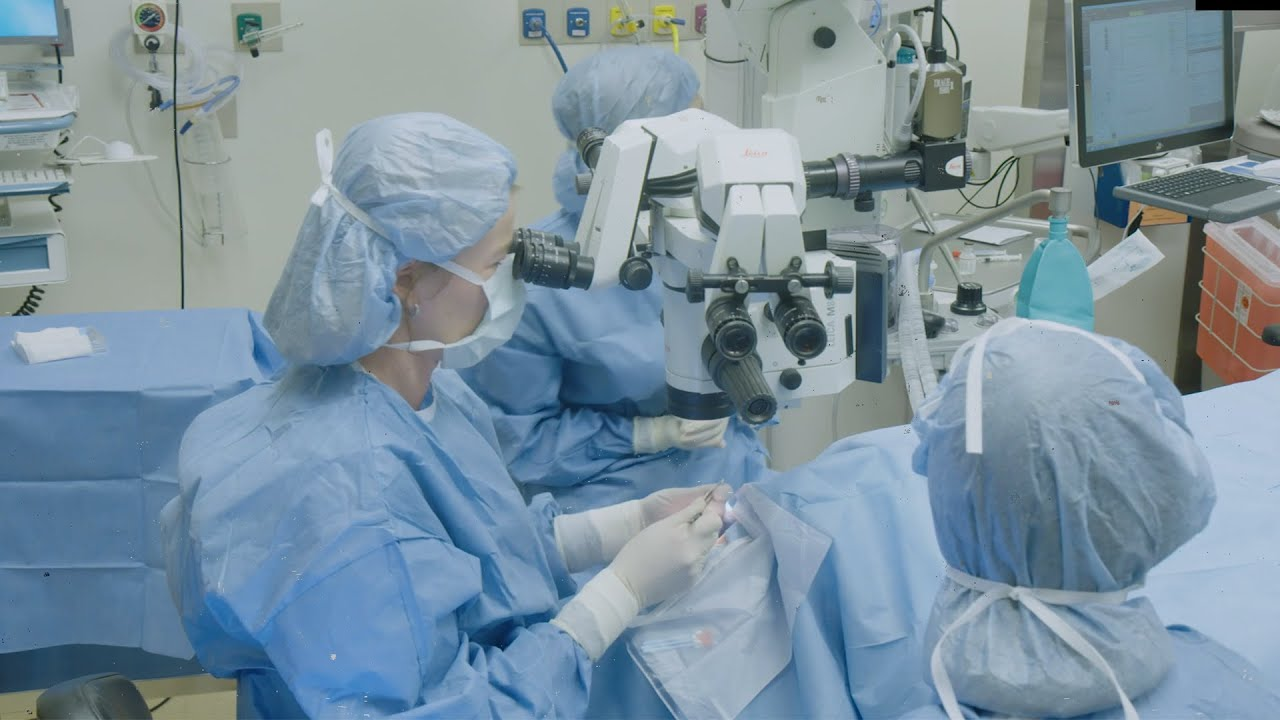
CALEC eye surgery, or cultivated autologous limbal epithelial cell therapy, represents a groundbreaking advancement in ocular regenerative medicine. Developed at Mass Eye and Ear, this innovative procedure harnesses the power of stem cell therapy to treat severe cornea damage, previously deemed irreparable. By extracting limbal stem cells from a healthy eye and cultivating them into a graft, CALEC eye surgery restores the cornea’s surface in patients suffering from debilitating ocular injuries. The results from clinical trials demonstrate more than 90% effectiveness, providing renewed hope for those affected by limbal stem cell deficiency. As the first human study funded by the National Eye Institute, this pioneering treatment may revolutionize cornea damage treatment and redefine possibilities for restoring sight.
Known alternatively as cultivated limbal stem cell therapy, CALEC eye surgery showcases the forefront of ocular rehabilitation methodologies. This innovative treatment focuses on regenerating the eye’s corneal surface using stem cells sourced from a patient’s own healthy eye, a process that has been meticulously refined through extensive clinical research. The successful application of limbal stem cells offers a viable option for individuals experiencing serious corneal injuries, paving the way for safe and effective solutions previously unavailable in traditional eye care. By engaging in comprehensive clinical trials, such as those conducted at Mass Eye and Ear, researchers aim to establish robust evidence supporting this transformative approach in ocular regenerative solutions.
Exploring CALEC Eye Surgery: The Future of Corneal Repair
CALEC eye surgery represents a groundbreaking advancement in ocular regenerative medicine, specifically designed to address severe corneal damage that traditional treatments fail to resolve. This innovative procedure utilizes cultivated autologous limbal epithelial cells, or CALEC, harvested from the healthy eye of the patient. During the trial conducted at Mass Eye and Ear, it was shown that this method not only restored corneal surfaces safely but also achieved remarkable success rates, with over 90% of patients benefiting from improved vision and pain relief.
The procedure’s design relies on cutting-edge stem cell therapy, establishing a new paradigm for treating conditions previously deemed untreatable. By expanding limbal stem cells into a cellular tissue graft, surgeons can effectively regenerate the damaged corneal surface, restoring clarity and function to the eye. As the trials continue to showcase the potential of CALEC, the hope is that this treatment will lead to widespread acceptance and incorporation into clinical practice to help more patients facing catastrophic corneal injuries.
Understanding Limbal Stem Cells and Their Role in Eye Health
Limbal stem cells play a vital role in maintaining the integrity and transparency of the cornea, acting as a natural barrier and renewal source for the eye’s outer surface. When damage occurs—such as through chemical burns or infections—these essential cells can be depleted, resulting in limbal stem cell deficiency. Such conditions can significantly impair vision and cause chronic pain, thereby necessitating innovative treatments like those demonstrated in the CALEC eye surgery trials.
Recent research highlights that restoring these vital cells can dramatically improve outcomes for patients with corneal damage. With advanced methodologies for isolating and cultivating these stem cells, researchers are optimistic about developing even more effective ocular regenerative medicines in the future. The ongoing clinical trials have laid a foundation for exploring not only the effectiveness of CALEC but also the broader applications of limbal stem cell therapy in treating a variety of ocular disorders.
The Success of Mass Eye and Ear’s Clinical Trial for CALEC
The success of the clinical trial at Mass Eye and Ear marks a significant milestone in the field of ophthalmology. Over 14 patients benefited from the CALEC treatment, showcasing high restoration rates of corneal surfaces. Using cutting-edge techniques, the research team demonstrated that almost half of the participants saw full corneal restoration within three months of the procedure, with continued improvements noted at later follow-ups.
This pivotal study not only emphasizes the safety and efficacy of CALEC but also paves the way for future research in ocular regenerative medicine. The collaboration between various institutions, including Dana-Farber and Boston Children’s Hospital, highlights the multidisciplinary approach necessary for tackling complex medical challenges. As more evidence accumulates, the hope is to establish CALEC as a standard treatment, greatly enhancing the quality of life for individuals suffering from severe corneal damage.
The Importance of Stem Cell Therapy in Regenerating Eye Tissues
Stem cell therapy has emerged as a leading solution for regenerating damaged eye tissues, paving the way for innovative treatments that can restore vision lost to injury or disease. The application of cultivated stem cells, particularly limbal epithelial cells, has been revolutionary in addressing corneal injuries. Unlike traditional treatments, which often focus solely on symptomatic relief, stem cell therapy targets the underlying cause by replenishing the diminished cell population in the eye.
As seen in the recent CALEC trials, this therapeutic approach can lead to significant restoration of visual acuity and corneal health. The implications for patients are profound, offering hope where previously little existed. This paradigm shift in treatment methodologies positions stem cell therapy as not only a viable alternative but potentially a definitive cure for certain types of corneal damage, heralding a new era in ocular care.
Clinical Trial Findings: Evidence Supporting CALEC Effectiveness
The clinical trial of CALEC surgery has delivered compelling evidence supporting its effectiveness in treating corneal damage. With over 90% success noted in trials, patients have experienced not just restoration of the cornea but also improved quality of life by alleviating pain and visual impairments. These positive outcomes underscore the potential of stem cell-based treatments to revolutionize care for patients with debilitating eye injuries.
Furthermore, the trial’s results demonstrate a high safety profile, with minimal adverse events occurring post-procedure. This is crucial as safety continues to be a top priority in any experimental therapy. With such promising findings, researchers are encouraged to pursue larger-scale studies to further validate the results and potentially expedite the process for FDA approval, allowing this innovative treatment to reach a larger patient demographic.
Future Prospects: Allogeneic Limbal Stem Cell Manufacturing
Looking ahead, the vision for CALEC eye surgery could expand significantly with the development of an allogeneic manufacturing process for limbal stem cells. This advancement would enable the use of stem cells from cadaveric donor eyes, which could potentially treat patients who have damage in both eyes—an area currently limited by the requirement of having a healthy donor eye for the biopsy.
By constructing a framework for broader access to limbal stem cell therapy, researchers aim to drastically widen the potential patient pool. This progress can lead to not just more patients receiving treatment, but also fostering collaborations across research institutions to streamline the manufacturing and application of these life-changing therapies in clinical settings.
Challenges Facing Ocular Regenerative Medicine
While the advancements in ocular regenerative medicine signal great hope, the field still faces significant challenges. One of the primary limitations is the necessity for a healthy eye to harvest limbal stem cells for the CALEC procedure, restricting eligibility. Moreover, the experimental nature of this treatment means that it is not yet widely available, with continued trials needed to meet regulatory standards.
The road to widespread adoption of such innovative therapies will require not only overcoming technical hurdles but also addressing ethical concerns, manufacturing capabilities, and access disparities. Stakeholder collaboration in the medical community will be essential to navigate these challenges as they work towards making CALEC therapy a standard practice in treating corneal injuries.
Patient Outcomes: Real-Life Impacts of CALEC Treatment
Patient outcomes following the CALEC treatment reveal the real-life impact of this innovative therapy. Many participants reported significant improvements in their vision and daily functioning following the procedure. These transformations are crucial for individuals who previously lived with debilitating corneal injuries, as they shift from a state of constant discomfort and visual impairment to one that allows for a more fulfilling life.
Moreover, the psychological benefits of improved vision cannot be underestimated. For many patients, the ability to see clearly again brings renewed hope and a sense of independence that had been lost due to their conditions. The success stories from the CALEC trials serve as powerful testimonials to the importance of continued investment and research in ocular regenerative medicine.
The Role of Regulatory Bodies in Advancing CALEC Treatments
Regulatory bodies, such as the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), play a critical role in the advancement of innovative treatments like CALEC. Their rigorous approval processes ensure that new therapies meet stringent safety and efficacy standards before being made available to the public. This regulation is especially relevant in the field of stem cell therapies, where ethical and safety considerations are paramount.
As researchers work towards submitting CALEC for federal approval, collaboration with regulatory bodies is vital. Early engagement with these entities can facilitate a clearer understanding of the necessary criteria for approval and expedite the path from research to clinical application. This proactive approach not only enhances the credibility of the treatment but also builds public trust in the emerging field of ocular regenerative medicine.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is CALEC eye surgery and how does it use stem cell therapy?
CALEC eye surgery refers to a specific stem cell therapy that involves transplanting cultivated autologous limbal epithelial cells to treat cornea damage. This innovative procedure uses stem cells harvested from a healthy eye, which are then expanded into a graft before being transplanted into the damaged eye, demonstrating over 90% effectiveness in restoring the corneal surface.
Who developed CALEC eye surgery and where was it first performed?
CALEC eye surgery was developed by researchers at Mass Eye and Ear, with the first procedure conducted by Ula Jurkunas, an associate director of the Cornea Service. This groundbreaking treatment was initially administered to patients at Mass Eye and Ear as part of a clinical trial.
What conditions can CALEC eye surgery treat related to cornea damage?
CALEC eye surgery effectively treats conditions resulting in corneal damage, such as chemical burns, infections, and trauma that lead to limbal stem cell deficiency. This deficiency often leaves the eye with a damaged surface that cannot recover without intervention.
What are limbal stem cells and their role in CALEC eye surgery?
Limbal stem cells are located at the limbus, the outer border of the cornea, and are essential for maintaining a healthy corneal surface. In CALEC eye surgery, these stem cells are extracted from a healthy eye and cultured to create a graft that can restore the damaged cornea.
How effective is CALEC eye surgery based on clinical trials?
Clinical trials for CALEC eye surgery indicated that the treatment achieved a success rate of over 90% in restoring corneal surfaces within 18 months. The procedure demonstrated significant improvements in vision and safety profiles among participants.
Is CALEC eye surgery currently available to patients?
As of now, CALEC eye surgery remains experimental and is not widely available in the U.S. Additional studies and clinical trials are ongoing to gather more data before seeking federal approval for broader implementation.
What future developments are planned for CALEC eye surgery?
Future developments for CALEC eye surgery include expanding the approach to allow for allogeneic manufacturing, which would use limbal stem cells from donor eyes. This could broaden the treatment’s availability for patients with damage to both eyes.
What safety concerns are associated with CALEC eye surgery?
The clinical trials for CALEC eye surgery reported a high safety profile, with no serious adverse events in donor or recipient eyes. Any minor occurrences, such as a bacterial infection related to contact lens use, were resolved quickly.
How is CALEC eye surgery supported by research funding?
CALEC eye surgery is funded by the National Eye Institute, which is part of the National Institutes of Health. It represents pioneering research in stem cell therapy for ocular applications, marking a significant advancement in ocular regenerative medicine.
What role does the Mass Eye and Ear clinical trial play in the advancement of CALEC eye surgery?
The Mass Eye and Ear clinical trial is critical in advancing CALEC eye surgery as it is the first of its kind, providing essential data on safety, efficacy, and outcomes for future studies aimed at achieving FDA approval and wider clinical use.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Overview of CALEC | CALEC stands for Cultivated Autologous Limbal Epithelial Cells, a stem cell therapy developed to treat severe corneal injuries. |
| Clinical Trial | Conducted at Mass Eye and Ear, involving 14 patients over 18 months, with over 90% success in restoring corneal surface. |
| Procedure | Involves a biopsy of healthy limbal epithelial cells, followed by lab expansion and surgical transplantation. |
| Success Rates | 50% of patients had complete restoration at three months; 93% by 12 months. |
| Safety Profile | No serious adverse events reported; one minor bacterial infection was noted. |
| Future Directions | Plans for larger trials and exploring donor cell sources to help patients with bilateral eye damage. |
| Regulatory Status | Currently experimental and not available at any U.S. hospital, further studies needed for FDA approval. |
Summary
CALEC eye surgery has emerged as a revolutionary and effective solution for patients with otherwise untreatable corneal damage. This innovative stem cell therapy not only addresses the core issue of limbal stem cell deficiency but also demonstrates remarkable success rates in restoring the corneal surface. As research continues and further clinical trials are conducted, we can anticipate broader applications and advancements in the treatment of eye diseases, potentially improving the quality of life for countless individuals facing visual impairment.